AVMs are rare, abnormal tangles of blood vessels in which connections form between arteries and veins directly (bypassing capillaries), disrupting the natural blood flow. AVMs can be congenital (present at birth) or may form during adulthood; they may also grow or disappear with time. The appearance of the AVM depends on the size of the blood vessel involved. The affected area may have a pink-blue tint, which can darken over time. You may feel some warmth in the area and the site may be painful. It may also pulse, ulcerate or bleed.
Extracranial AVMs exist outside the skull and intracranial AVMs occur inside the skull. Intracranial AVMs may affect blood flow directly to the brain and could cause stroke. AVMs also may cause congestive heart failure if large amounts of blood flow rapidly through them. Deformities that can affect your vision and ability to swallow may also result from an AVM.
- Diagnosis of Arteriovenous Malformations of the Head, Neck and Face-
Your physician will perform a physical exam and may order one or more of the following diagnostic imaging tests.
A Duplex or Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to image your blood vessels and measure your blood-flow speed.
Computed tomography angiogram (CTA) uses a contrast agent (dye), which is injected into your vessels, to look for abnormalities. CT scans that do not use dye may also be taken of your head and neck.
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) combines an injected contrast agent (dye) with magnetic and radio waves to create 3-D cross-sections of the arteries in your neck and brain. An MRI (without dye) creates images of your head and neck.
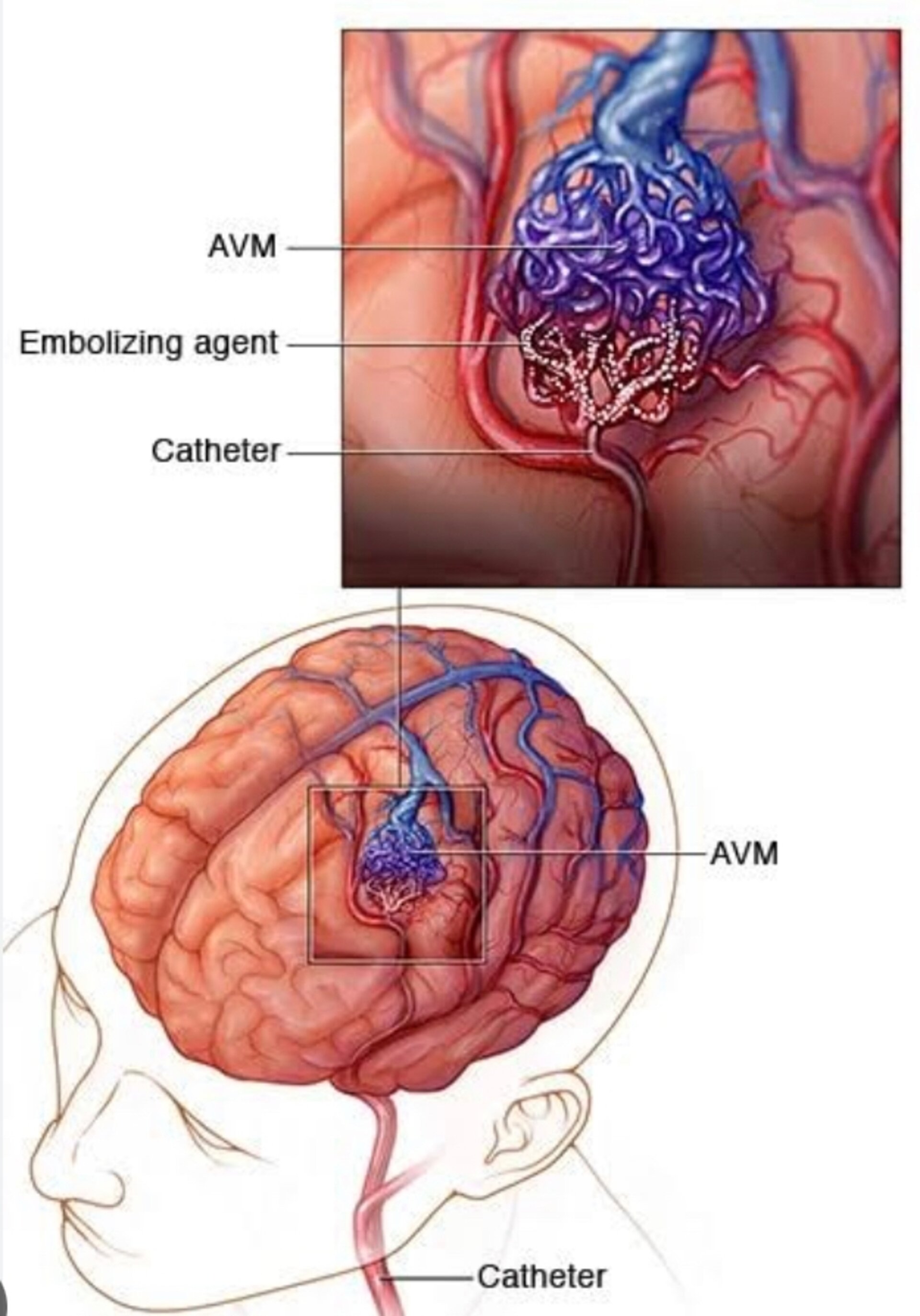
In a catheter angiogram, the surgeon inserts a thin catheter through your groin and threads it into your carotid arteries; a contrast agent (dye) is injected to help clinicians visualize the arteries on X-rays.
- Treatment Options for Arteriovenous Malformations of the Head, Neck and Face-
Finding the best treatment option for an AVM depends on its location and pattern of blood flow. If your AVM is not disfiguring or causing complications or pain, your doctor may suggest observation. If it is disfiguring, bleeding, ulcerating or causing pain or discomfort, you may be advised to undergo surgery or embolization.
Get in touch with Dr. Pushan Sharma, amongst the leading Neuro Vascular Intervention Specialist in Praygraj, UP.